Low Cost AGV Solutions for Fast Production Line Integration
For many small and medium-sized enterprises, introducing AGV electric transfer carts to improve production efficiency is an attractive option, but the high investment costs and long adaptation periods can be daunting. In fact, with the right approach, it is not difficult to adapt AGV to existing production lines at low cost and quickly.
How to Choose AGV?
Small and medium-sized enterprises typically have limited production space and relatively fixed production processes. In such cases, there is no need to choose a customized AGV with complex functions from the outset.
A standardized, modularly designed general-purpose AGV is a better choice. Such equipment is more affordable and has basic expansion interfaces that can be adapted to most common production scenarios.
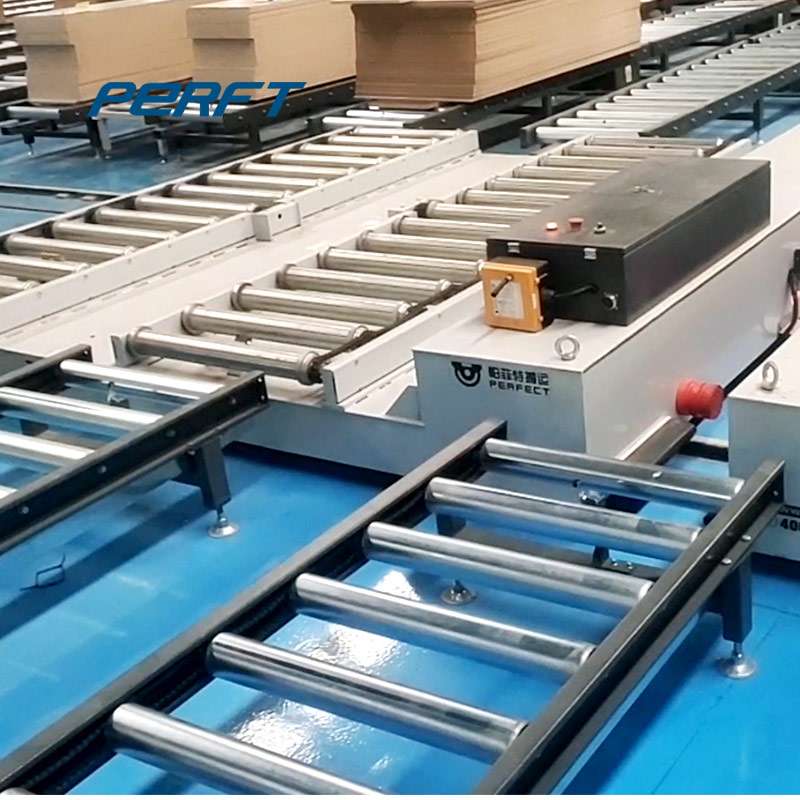
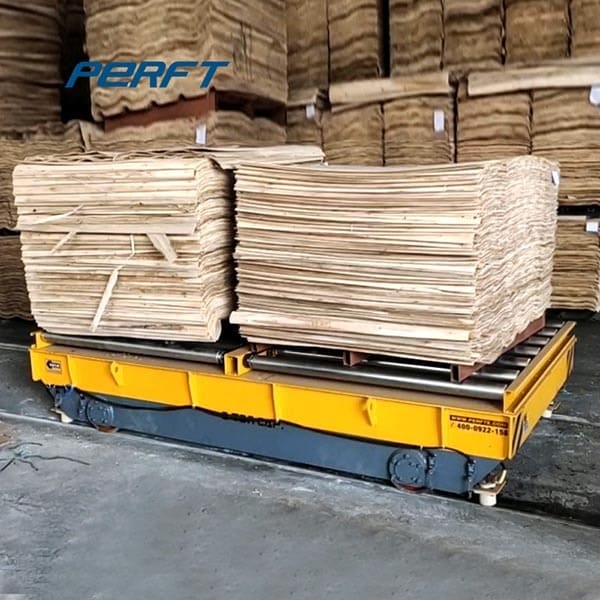
For example, selecting automated guided vehicle trolley with standardized pallet interfaces not only allows compatibility with existing pallets in the workshop but also enables integration with conveyor belts, shelves, and other basic equipment, eliminating the need to modify material containers specifically for AGV.
15 Ton Capacity AGV Video
What Are the Best AGV Navigation Options?
When it comes to choosing a navigation method, flexibility is key, as it can effectively reduce renovation costs.
Traditional magnetic navigation and QR code navigation are relatively low-cost options with minimal requirements for floor modifications. If the workshop floor is made of cement or wear-resistant flooring, simply applying navigation QR codes or magnetic strips directly to the floor is sufficient. This method is simple and cost-effective, with installation typically completed within one or two days.
If you are concerned that installing navigation markers on the floor may obstruct the movement of manual forklifts, laser navigation AGV are a viable alternative. They require minimal floor modifications, as they locate themselves by scanning existing workshop equipment, columns, and other fixed objects. By pre-mapping the workshop layout using software and setting path parameters in advance, they can be operational quickly.
How to Add AGV Without Major Line Changes?
Many small and medium-sized enterprises have built their production lines gradually over the years, resulting in irregular equipment layouts. In such cases, there is no need for large-scale renovations to the existing production line. Instead, “localized fine-tuning” can replace “complete reconstruction.”
By simply installing a low-cost positioning barrier or sensor next to the workstations where AGV need to dock, material handling cart can achieve precise docking.
Reserving a width of 80–100 centimeters at the corners of the operating route ensures smooth turning for AGV. This way, there is no need to move large production equipment to meet the operational requirements of AGV.
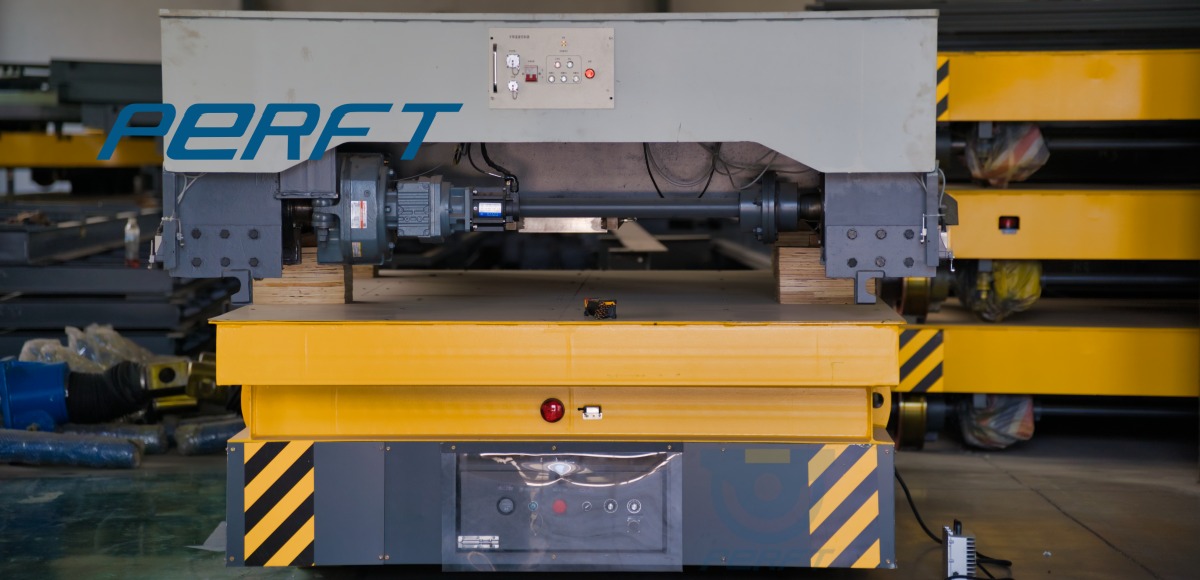

How to Simplify AGV Software Integration?
The production management systems of small and medium-sized enterprises may be relatively basic, so there is no need to spend a lot of money on complex AGV scheduling systems.
Instead, opt for an AGV control system that supports simple API interfaces, as long as it can integrate with existing ERP or MES systems for basic data exchange. For example, production tasks can be imported via Excel spreadsheets, or scheduling instructions can be manually issued using a tablet.
In the early stages, AGV can even operate independently of complex systems, following pre-set routes to move materials on a fixed schedule, first addressing the “last-mile” issue of material handling, with system functionality upgraded gradually over time.
How Can Existing Equipment Work with AGV?
By fully utilizing the existing material containers and auxiliary equipment in the workshop, the adaptation costs for electric platform trolley can be significantly reduced.
Common workshop containers and material racks, if standardized in size, can be directly loaded onto AGV without the need for custom-made pallets.
At the interface between conveyor belts and AGV, simple ramps or transition platforms can replace expensive automatic docking devices. As long as the height difference is kept within 5 centimeters, automated guided vehicle trolley can smoothly load and unload materials. These minor modifications are cost-effective yet enable automated guided vehicle trolley to seamlessly integrate into existing material handling processes.
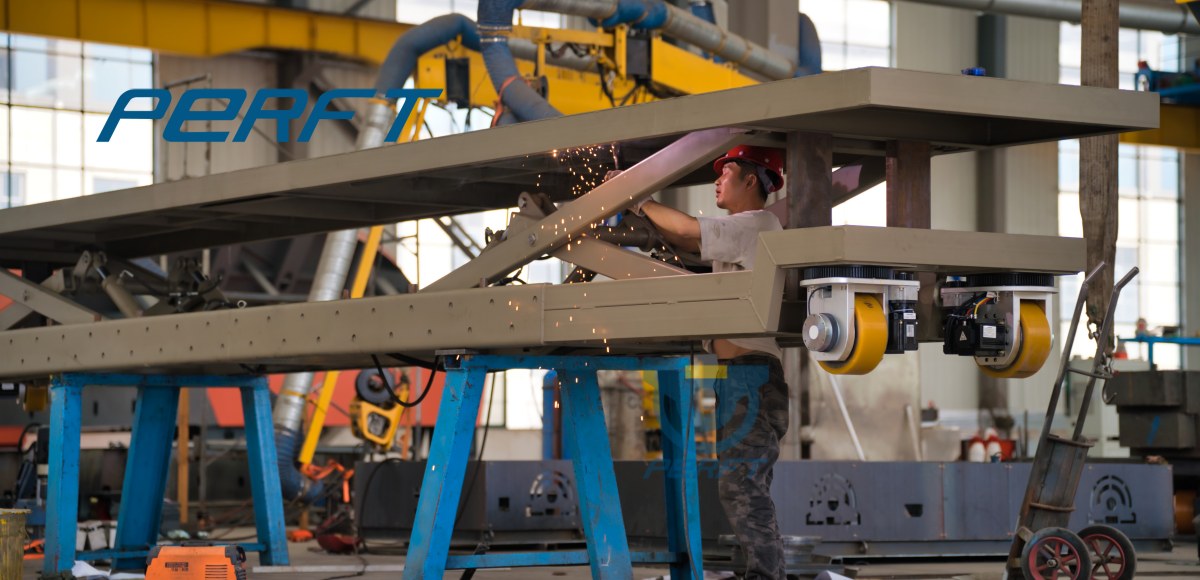

Why Use a Step-by-Step Approach for AGVs?
Implementing in phases can effectively reduce initial investment and adaptation risks.
You can start by piloting a specific segment of a production line, such as material transportation from the warehouse to the assembly workstation, using 1-2 automated guided vehicles to validate the process. After verifying the compatibility, you can gradually expand to other stages.
This approach allows you to identify and address issues promptly, avoid excessive upfront investment, and enable employees to gradually familiarize themselves with automated guided vehicle trolley operation and maintenance, laying the groundwork for full-scale implementation.