Rail Transfer Cart (RGV) Guide: Types, Applications & Maintenance Tips
Rail cart plays a key role as material handling equipment. With the characteristics of high efficiency, stability, and reliability, it is busy in factory production lines, logistics warehouses, and other scenes. But for many people, rail transfer cart still has a lot of questions.
Common Types of RGV
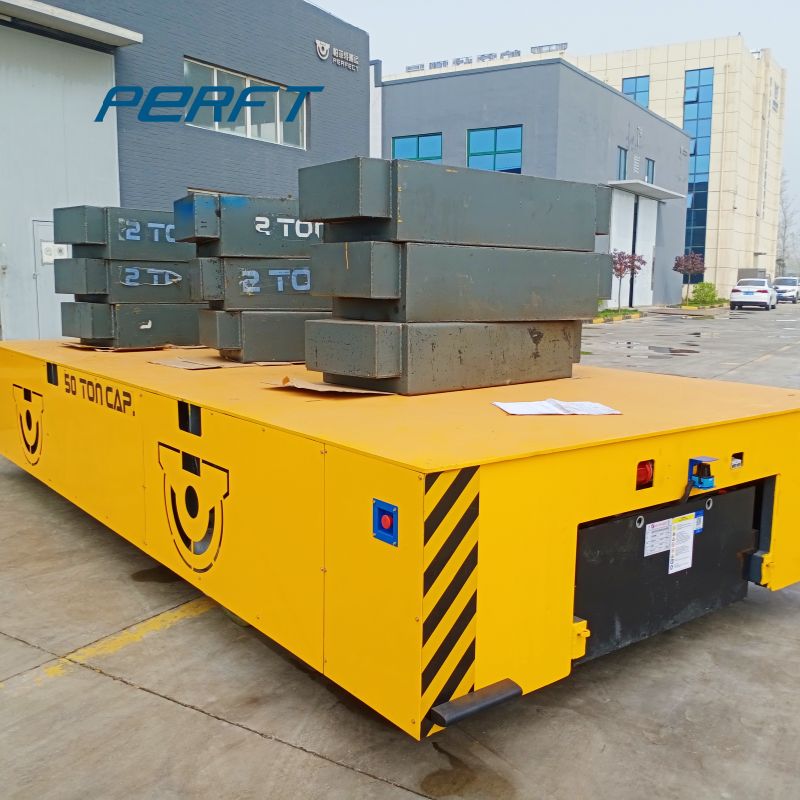
According to different functions, electric rail transfer cart is mainly divided into assembly-type RGV systems and transport-type RGV systems.
- The assembly type RGV system focuses on assisting the assembly of parts on the production line, and can accurately transport the required parts to the designated assembly stations to improve assembly efficiency and accuracy.
- The transport type RGV system mainly undertakes the task of transporting a large amount of materials, and shuttles back and forth between warehouses and production lines and different production areas to ensure the timeliness of material supply.
Transfer Cart Factory Video
Application of RGV
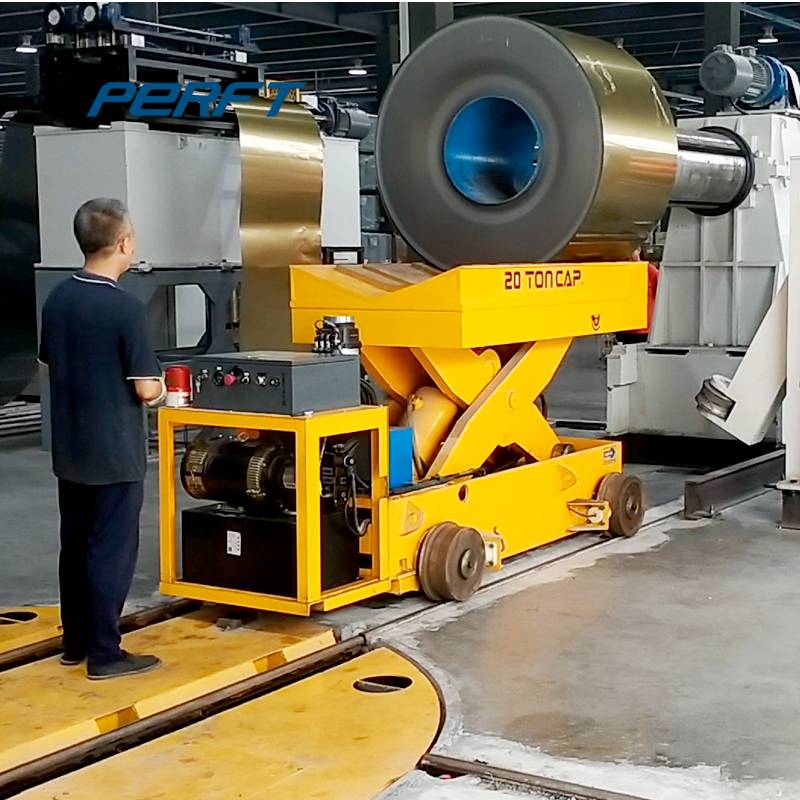
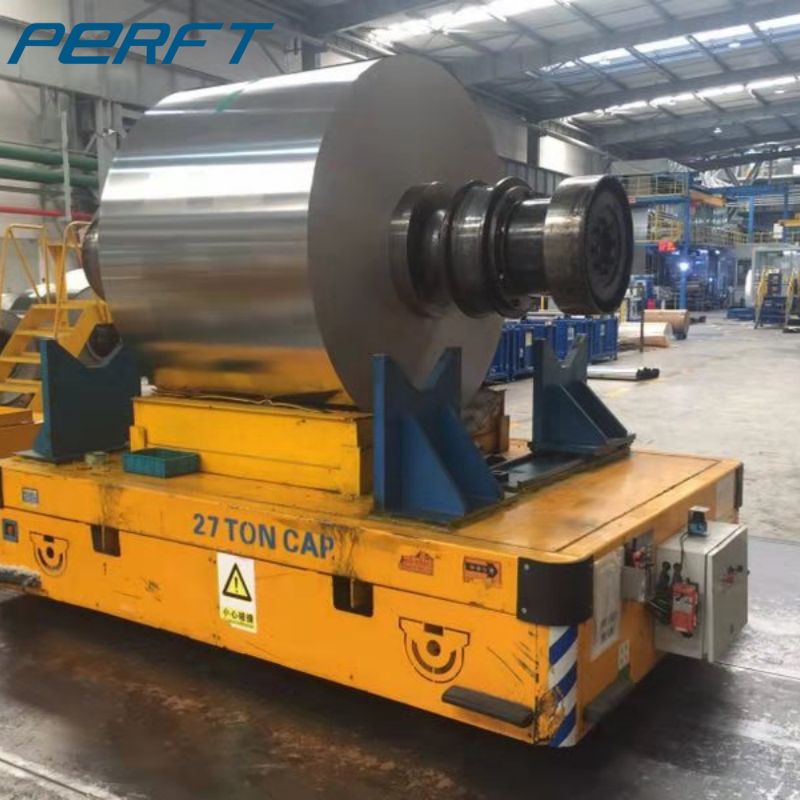
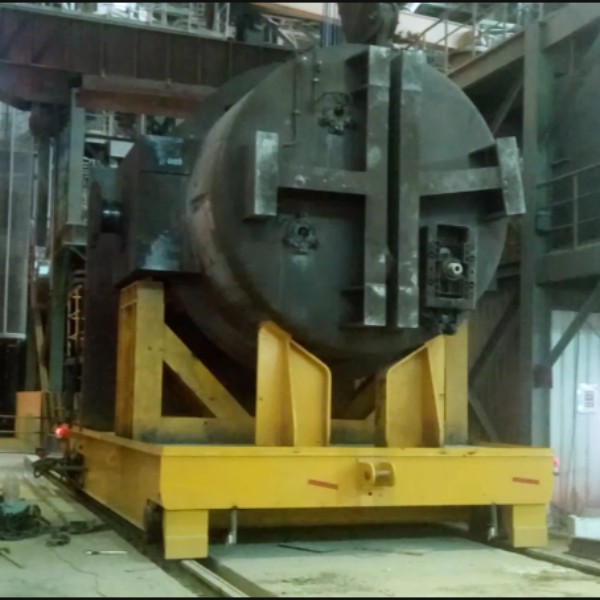
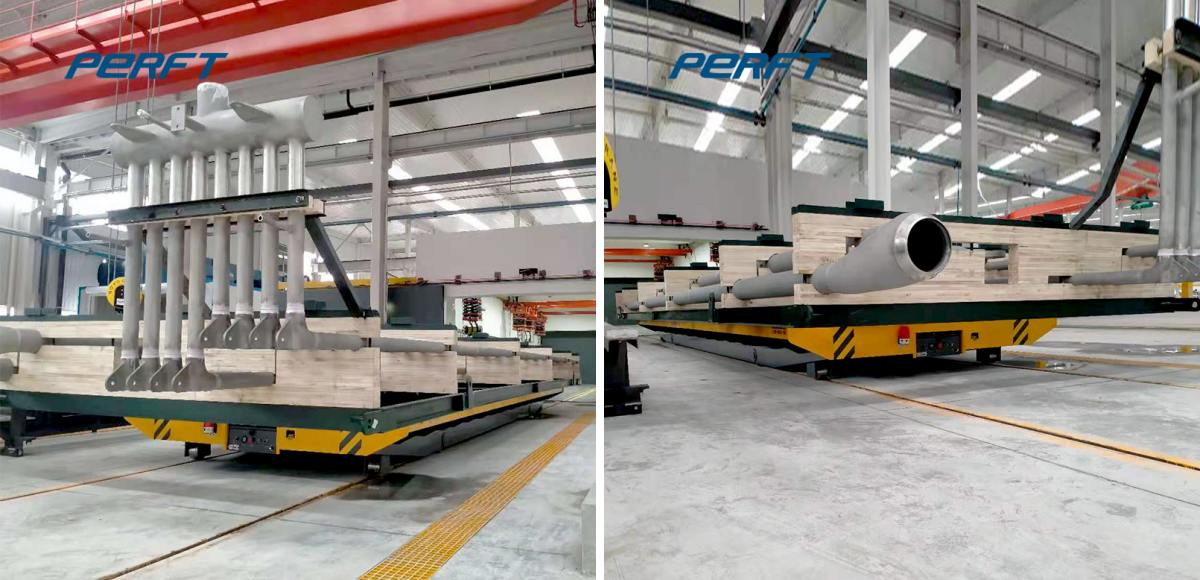
From the point of view of application scenarios, in factories, it is the main force of material handling in production lines. For example, in automobile manufacturing factories, electric rail transfer carts can move automobile parts from the warehouse to various assembly lines to ensure the coherence of the production process.
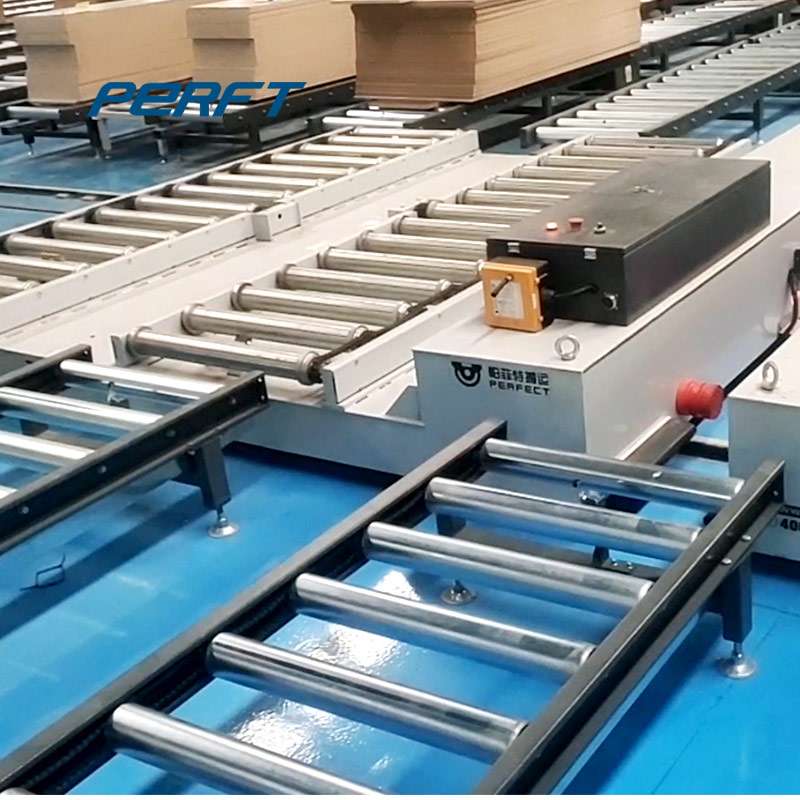
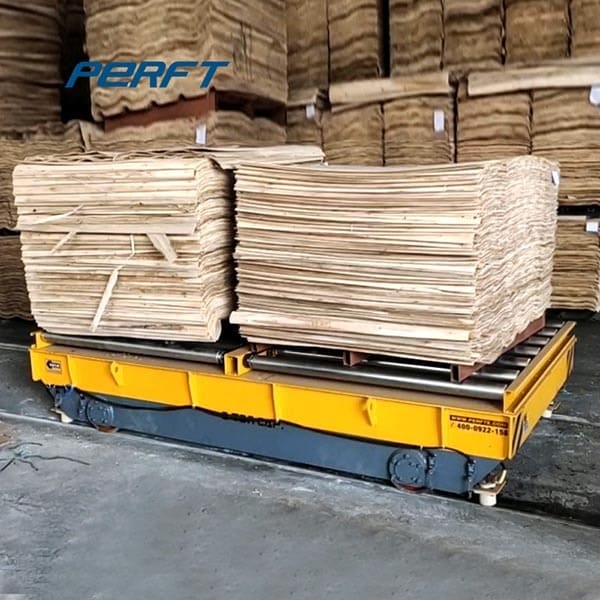
In logistics warehouses, it can realize the rapid access to and transfer of goods between storage areas, and improve the space utilisation rate of warehouses and the turnover rate of goods. Like some large-scale e-commerce warehousing centre, RGV with automated warehousing system, can quickly and accurately complete the sorting and distribution of goods.
Working Principle of RGV
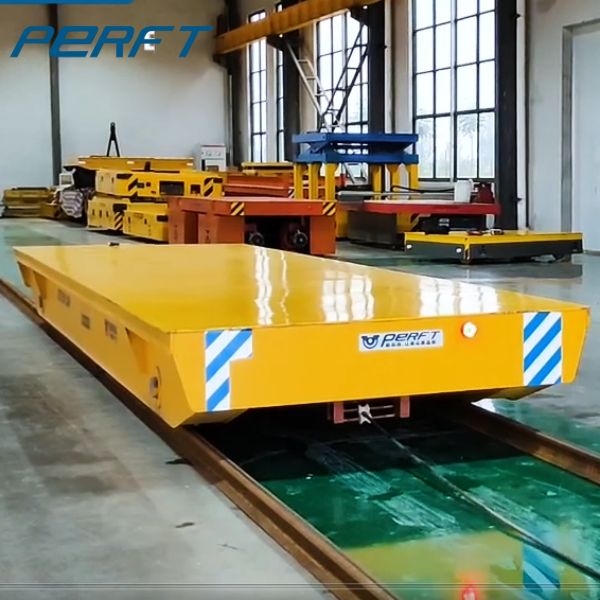
Rail transfer cart is based on the track operation, through the motor drive wheels on the track, forward, backward, stop, and other actions. Its working principle is not complicated, just like our common tram, except that RGV is tailor-made for industrial material handling. The motor provides power through the transmission device to drive the wheels to rotate, so as to achieve transfer cart on the track.

Control Mode of RGV
The control mode is mainly divided into two modes: manual and automatic. In manual mode, the operator controls the running direction and speed of rail cart by operating the handle or remote control, which is suitable for some temporary and highly flexible handling tasks, or used in the debugging and maintenance of the equipment.
In automatic mode, RGV is the ‘intelligent brain’, which communicates with the host computer or WMS (Warehouse Management System), receives commands, combines with RFID, barcode, and other identification technologies, and automatically completes the material handling tasks. In factories with a high degree of automation, rail transfer carts can work 24 hours a day in accordance with preset procedures in automatic mode, greatly improving production efficiency.
Operation and Maintenance of RGV
Stable operation and efficient maintenance are the key to the long-term, reliable operation of RGV. In daily use, rail cart should be inspected and maintained regularly. Wheels, as the parts in direct contact with the track, need to be paid attention to the wear and tear situation. Regularly check the thickness of the wheel rims and the degree of wear of the tread surface, and replace the wheels with serious wear in time to prevent derailment and other accidents from happening.
Drive motor is also the focus of maintenance, check the appearance of the motor with or without damage, whether the cooling fan is running normally, and regularly test the insulation resistance of the motor winding to ensure stable motor performance. Connecting cables should not be ignored; check the cable outer skin for scratches and wear, especially the bending parts and joints, to ensure stable signal transmission. In addition, it is also necessary to regularly clean the debris, dust, and oil on the track to ensure that the track is clean and flat, which is crucial to the smoothness and accuracy of rail transfer cart operation.